What is E509?
Complete guide to understanding E509 (Calcium Chloride) in your food
The Quick Answer
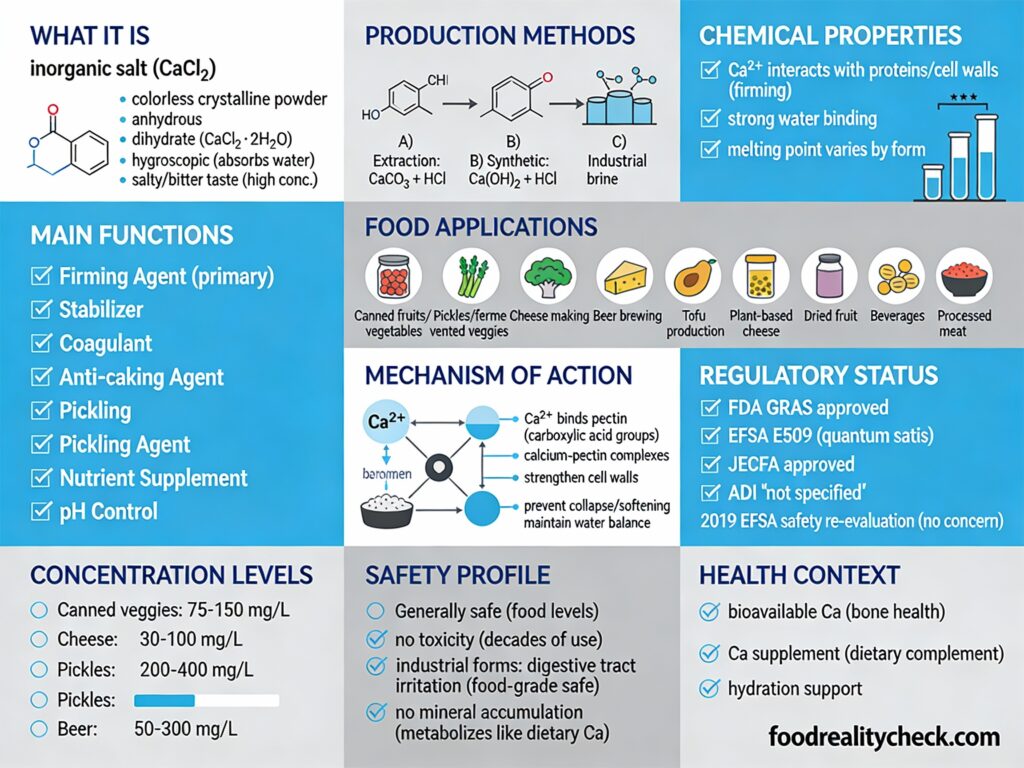
E509 is a mineral salt used as a firming and stabilizing agent.
It’s used in food to keep vegetables firm, help cheese curdle properly, and maintain texture in processed foods.
It’s also a natural source of calcium, found in your body and in nature.
📌 Quick Facts
- Category: Inorganic mineral salt (firming agent, stabilizer)
- Chemical Name: Calcium Chloride (CaCl₂)
- Found in: Cheese, pickled vegetables, canned fruits, sports drinks, dairy products
- Safety: Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) by FDA and EFSA
- ADI (JECFA): “Not specified” – no safety limit needed
What Exactly Is It?
E509 is made from calcium and chloride—two naturally occurring elements.
Its chemical formula is CaCl₂ (one calcium atom and two chloride atoms).
It appears as a white, odorless, crystalline solid that dissolves easily in water.
When dissolved, it separates into calcium ions (Ca²⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻), the same minerals your body uses for muscle function and bone health.
Where You’ll Find It
E509 appears in many common foods:
• Cheese and dairy products (especially ripened cheese)
• Pickled vegetables (pickles, olives, capers)
• Canned or bottled fruits and vegetables
• Jams, jellies, and marmalades
• Sports drinks and electrolyte beverages
• Tofu and plant-based products
• Beer and brewing applications
• Chocolate and caramel fillings
• Meat processing and tenderization
• Dehydrated and powdered milk
It’s especially common in cheese making and preserved vegetables.
Why Do Food Companies Use It?
E509 has multiple important functions in food processing:
In cheese making: Pasteurization removes natural calcium from milk, making it difficult for rennet to form firm curds. E509 restores calcium levels, allowing proteins to bond properly and creating firmer cheese with better yield and texture.
In preserved vegetables: E509 acts as a firming agent, keeping canned or pickled vegetables crisp and firm rather than mushy. It maintains color and prevents texture degradation during storage.
In sports drinks: E509 is a source of bioavailable calcium and an electrolyte that supports hydration and muscle function.
In confectionery: E509 lowers the freezing point of water, allowing caramel and chocolate centers to freeze properly without being solid throughout.
Is It Safe?
Yes, E509 is considered very safe by all major regulatory bodies.
The FDA classifies it as “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) with no limits on use in most food applications.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) re-evaluated it in 2019 and found no safety concerns at reported use levels.
The WHO Expert Committee (JECFA) assigned it an ADI of “not specified,” meaning no toxicological limit is necessary—it’s considered inherently safe even at high levels.
What Are The Health Concerns?
E509 has virtually no documented health concerns. Scientific research shows:
Toxicity: Classified as “low acute and short-term oral toxicity” with no adverse effects at normal food levels
Genotoxicity: No genetic damage observed—any in vitro effects only occurred at unrealistic concentrations incompatible with human physiology
Carcinogenicity: No tumor formation or cancer risk observed in animal studies
Reproductive toxicity: No adverse effects on reproduction or fetal development
Natural occurrence: Calcium and chloride are essential minerals already present in your body—you’re not consuming a foreign substance
E509 is actually used medically to treat calcium deficiency and even in emergency treatment for certain types of poisoning.
Natural vs Synthetic Version
E509 is a naturally occurring inorganic mineral compound.
While the food-grade version is manufactured in a facility (processed from natural mineral sources or synthesized), the chemical itself is identical to naturally occurring calcium chloride found in seawater and mineral deposits.
It’s not “synthetic” in the sense of being a completely artificial creation—it’s a natural mineral refined for food use.
Natural Alternatives
Want to avoid E509?
Many foods naturally contain calcium and can be used instead:
• Milk and dairy – natural source of calcium and protein for cheese making
• Gelatin – natural gelling agent (instead of using firming agents)
• Lemon juice or vinegar – natural acidity regulators for pickling
• Agar-agar or pectin – natural thickeners and gelling agents
• Sea vegetables – natural source of minerals
However, these alternatives are less consistent and more expensive, which is why E509 remains standard in commercial food production.
The Bottom Line
E509 is a naturally occurring mineral salt that’s been used in food for centuries and is considered one of the safest food additives available.
It’s approved worldwide by the FDA, EFSA, and WHO with no safety limits—a distinction reserved only for truly non-toxic substances.
Calcium and chloride are essential minerals your body needs, so consuming E509 is not introducing a foreign chemical.
For cheese lovers, pickle enthusiasts, and anyone who drinks sports drinks, E509 has likely been part of your diet for years without any concern.