How Is Sea Salt Harvested? The Journey from Ocean to Table
From seawater to crystallized mineral treasure.
The Overview
Sea salt production is one of the oldest methods of harvesting salt, unchanged in principle for centuries.
The process harnesses sun and wind to evaporate seawater, leaving behind crystallized sodium chloride and natural minerals.
Here’s exactly what happens from ocean to your kitchen table.
🥘 Main “Ingredients”
• Seawater
• Sunlight
• Wind
• Time
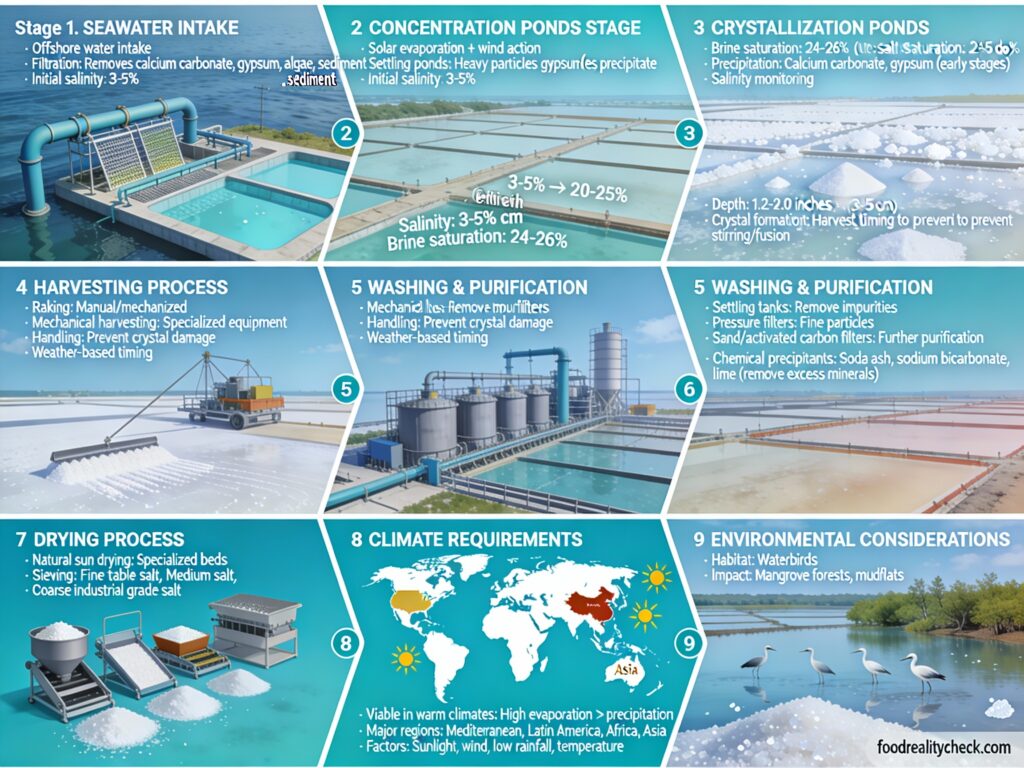
Step 1: Seawater Collection & Pumping
Fresh seawater is drawn directly from the ocean through underground or surface channels into settling ponds.
This first stage allows sand, debris, and other large particles to settle out naturally.
The water is calm and ready for the concentration phase.
Step 2: Pond Preparation & System Setup
Before the harvest season, farmers restore salt field systems by rolling and leveling hardened soil.
An even surface is critical—uneven ground causes water to pool in low spots and dry too quickly elsewhere.
This preparation ensures uniform crystallization across all ponds.
Step 3: Concentration Phase
Seawater is moved through concentration ponds where sun and wind gradually evaporate water.
Salinity rises naturally from 3-5% to approximately 20-25% over days or weeks.
Heavy impurities like calcium carbonate and gypsum precipitate out early, ensuring only salt crystallizes later.
Step 4: Crystallization Phase
Concentrated brine is transferred to crystallization ponds where salt saturation reaches critical levels (around 250 g/l).
Under continuous sun and wind exposure, sodium chloride crystals slowly form on the pond floor.
This takes 2-5 days, gradually building a bright white crystalline layer.
Step 5: Harvesting the Salt
Once the crystal layer reaches sufficient thickness, harvesting begins—with surprisingly little effort required.
Brine acts as a natural lubricant, allowing salt to detach easily from the pond floor.
Large wooden or metal rakes gather salt into piles, draining off excess seawater.
Modern Mechanical Harvesting
Step 6: Machine Harvesting (Industrial Scale)
On large-scale salt fields, self-propelled mechanical harvesters integrate three functions: raking, collecting, and transporting.
Front-mounted cutting blades push crystallized salt toward a center conveyor, which lifts it into storage tanks holding several tons.
This dramatically reduces harvesting time while improving transport efficiency across massive operations.
Step 7: Washing & Cleaning
Machine-harvested salt contains natural impurities like sand, mud, and crushed shells.
Salt is transported to washing stations where rotating screw agitators churn it in water, flushing away contaminants.
Hand-harvested artisanal salt often skips this step, retaining more minerals.
Step 8: Stacking & Storage
Cleaned salt is loaded onto mechanical stackers that pile it into towering white mountains in storage yards.
This organized stacking simplifies quality control, inventory management, and preparation for further processing or shipping.
Salt can be stored this way for extended periods without degradation.
Why This Process?
Solar evaporation is the oldest and most eco-friendly method of salt production, requiring no fossil fuels or drilling.
It produces high-quality crystals with natural mineral content (magnesium, potassium, iron) that table salt lacks.
And it keeps production costs competitive while maintaining sustainability for large-scale commercial operations.
What About Processing & Additives?
Most commercial sea salt includes:
• Anti-caking agents – to prevent moisture absorption
• Iodine – for nutritional fortification
• Filler additives – in some table salt varieties
Hand-harvested artisanal sea salt often contains none of these.
Premium “fleur de sel” (flower of salt) is collected from the surface of ponds and remains completely natural.
The Bottom Line
Sea salt harvesting is a natural, time-honored process that harnesses sun, wind, and evaporation to extract mineral-rich crystals from the ocean.
It’s designed for sustainability, quality, and the gentle extraction of salt while preserving beneficial minerals.
Now you know exactly how seawater becomes the salt that seasons your food.