What is E462?
Complete guide to understanding ethyl cellulose in your food
The Quick Answer
E462 is ethyl cellulose, a plant-based thickener and stabilizer derived from cellulose.
It’s used to improve texture, prevent separation, and create protective coatings in sauces, supplements, and processed foods.
Most people who consume processed foods, dietary supplements, or sauces regularly encounter trace amounts of it.
📌 Quick Facts
- Category: Thickener, Stabilizer & Film Former
- Found in: Dietary supplements, sauces, salad dressings, frozen products, baked goods
- Safety: FDA-approved (GRAS), EFSA-approved, no ADI needed
- Approved by: FDA, EFSA, JECFA
- Key Fact: Water-insoluble, plant-based cellulose derivative
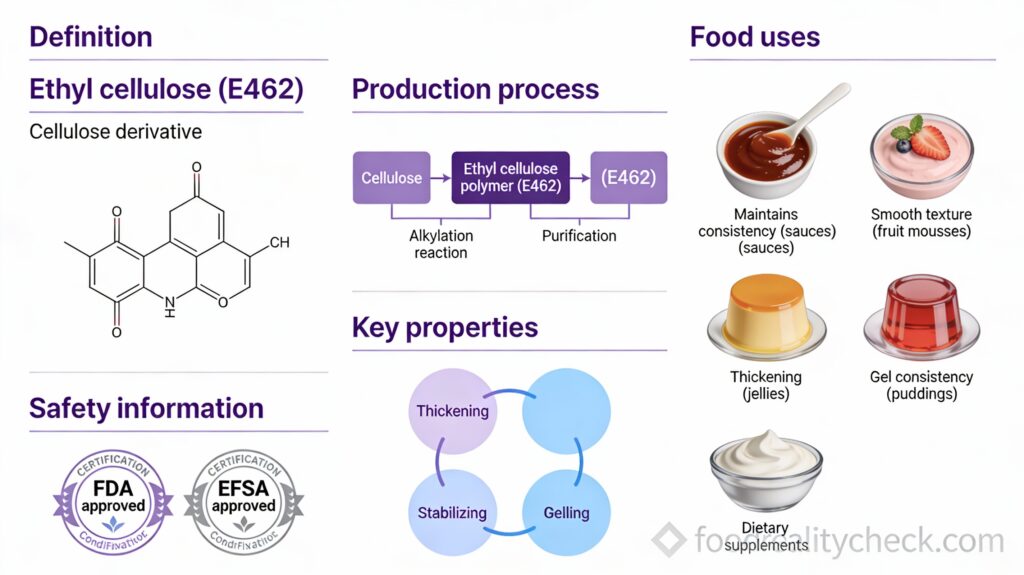
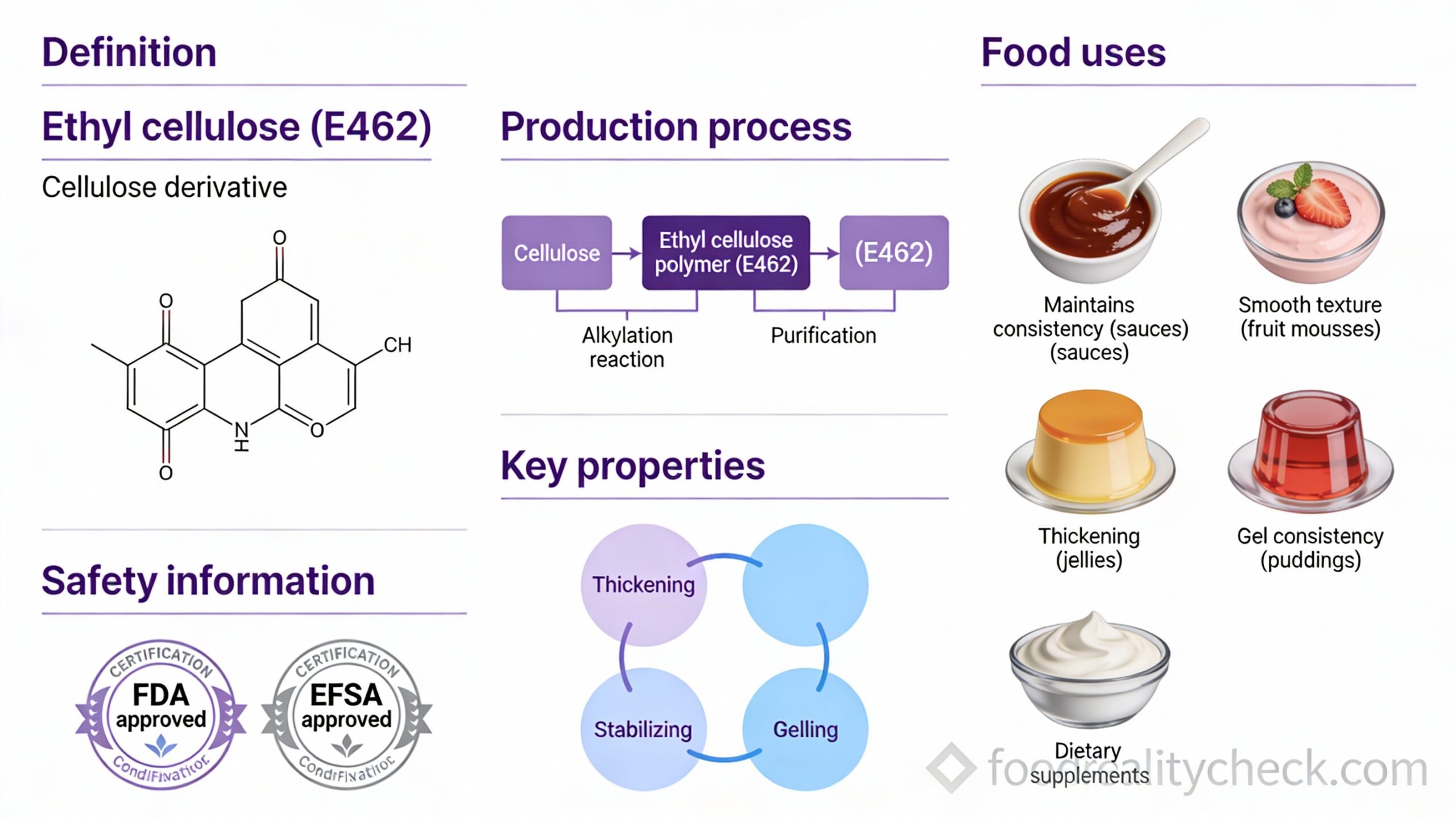
What Exactly Is E462?
E462 is ethyl cellulose, a plant-derived thickener and stabilizer created from cellulose—the main structural component of plant cell walls.
More specifically, cellulose from plant materials (wood chips or plant fibers) is chemically modified by attaching ethoxyl groups (-OC₂H₅). This semisynthetic process creates a water-insoluble compound with unique properties useful in food production.
E462 appears as a white granular powder that is virtually odorless and tasteless. A critical property distinguishing it from other cellulose derivatives is that it’s insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents.
In technical terms, it’s a nonionic polymer that thickens liquids, stabilizes emulsions, forms protective coatings, and binds ingredients. Its water-insoluble property makes it particularly valuable for applications requiring moisture barriers.
Where You’ll Find E462
E462 appears in numerous processed foods and supplements requiring specialized functions:
– Dietary food supplements (solid form)
– Salad dressings
– Pizza preparations
– Sauces and gravies
– Frozen products
– Baked goods
– Cheese products
– Meat and sausages
– Dairy products
– Pasta
– Confectionery and sweets
– Fruit mousses and desserts
– Jellies and gel products
– Puddings
E462 is particularly common in dietary supplements where it’s used as a tablet binder and coating agent.
💡 Pro Tip: Look for “Ethyl cellulose,” “Ethylcellulose,” or “E462” on ingredient lists. It’s especially common in dietary supplement tablets and powders where its water-insoluble property provides protection and acts as a binding agent.
How E462 Works in Food
E462 serves multiple critical functions in food production.
As a thickener: E462 increases the viscosity of liquids, giving them desired texture and mouthfeel. In sauces, dressings, and desserts, it creates the appropriate consistency.
As an emulsion stabilizer: E462 prevents separation of oil and water phases in complex mixtures. In salad dressings, for example, it maintains homogeneous consistency and prevents ingredients from separating.
As a film former: E462’s most distinctive feature is its water-insoluble property. It creates protective coatings that act as moisture barriers and oxygen barriers. In pizza preparations, for example, it creates a barrier layer that controls how ingredients diffuse into other layers.
As a binder and filler: In dietary supplements and other products, E462 binds ingredients together and provides bulk.
As a taste masking agent: In supplements with unpleasant flavors, E462 helps mask off-flavors.
Why Do Food Companies Use E462?
E462 solves specific technical problems that other additives cannot address as effectively.
Its water-insoluble property is particularly valuable. Unlike water-soluble thickeners, E462 maintains barrier properties and protects ingredients from moisture exposure. This is critical in dietary supplements, where tablets must remain stable despite humidity exposure.
In sauces and dressings, E462 prevents separation better than many alternatives. In coated products, its ability to form protective coatings makes it superior to water-soluble competitors.
Is It Safe?
Regulatory authorities confirm E462 is safe for food use.
The FDA classified ethyl cellulose as “Generally Recognized As Safe” (GRAS) in 2013, approving it for use at levels ranging from 0.0075 to 5% in various foods. The EFSA conducted a comprehensive re-evaluation in 2017-2018 and concluded there is “no need for a numerical ADI” and “no safety concern at reported uses and use levels.”
JECFA set the ADI as “not specified”—indicating no numerical limit is needed because safety is assured.
✓ Safety Confirmed: The EFSA’s 2017-2018 re-evaluation confirmed no safety concern for E462. No numerical ADI is needed, indicating exceptional safety. Actual exposure at approved use levels is far below any threshold for concern.
The EFSA’s 2017-2018 Comprehensive Safety Re-evaluation
The European Food Safety Authority’s thorough 2017-2018 re-evaluation of all cellulose derivatives provides authoritative reassurance.
Key findings:
– No numerical ADI needed for E462—indicating exceptional safety
– No safety concern at reported uses and use levels
– Comprehensive toxicological data reviewed and determined acceptable
– EFSA evaluated all celluloses (E460-E469) together; E462 specifically cleared
The 2017-2018 EFSA Panel concluded that safety is assured at all approved use levels.
Understanding Recent Research
Important context about recent observational studies:
In 2023, a large BMJ study examined emulsifier intake and cardiovascular disease risk. The study found associations between certain celluloses (E460 and E466) and CVD risk. However, E462 was NOT individually analyzed in this study.
Why not analyzed? E462 was consumed by less than 5% of study participants, making statistical analysis impossible. This is a limitation of the study’s population, not an indication that E462 is unsafe or concerning.
Critical point: E462’s absence from identified risk associations reflects low consumption in the study population, not safety problems.
The Water-Insoluble Property—A Key Advantage
E462’s water-insoluble property distinguishes it from many other cellulose additives.
Unlike E463, E464, E465, and E466 (which dissolve in water), E462 remains insoluble. This property makes it particularly valuable for:
– Creating protective moisture barriers
– Forming oxygen-resistant coatings
– Protecting supplement tablets from humidity
– Creating barrier layers that control ingredient diffusion
– Sustained-release pharmaceutical coatings
Pharmaceutical Use—Decades of Safe History
E462 has extensive use in medications spanning decades.
Ethyl cellulose is the most common pharmaceutical coating for sustained-release medications. It’s used to create coatings that slowly release drugs over time, improving treatment efficacy. Because it doesn’t swell when exposed to water, it impedes water penetration and controls drug release rates precisely.
E462 is also used as a binder in vitamin and mineral tablets and as a component of protective coatings. This extensive pharmaceutical use—involving millions of people—provides real-world evidence of safety.
Plant-Based and Dietary Attributes
E462 is entirely plant-based with excellent dietary compatibility:
– Vegan ✓
– Vegetarian ✓
– Gluten-free ✓
– Kosher pareve ✓
– Plant-based ✓
E462 is derived from cellulose sourced from plant materials (wood chips and plant fibers), making it suitable for all dietary preferences.
Manufacturing Process
E462 is manufactured through controlled chemical synthesis using plant-derived cellulose.
Step 1 – Alkalinization: Cellulose is treated with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), which prepares it for chemical modification.
Step 2 – Etherification: Ethyl chloride is added to attach ethoxyl groups (-OC₂H₅) to the cellulose. Different grades can be created by controlling the number of ethoxyl groups added—the ethoxyl content determines viscosity and other properties.
Food-grade E462 must contain ethoxyl groups between 44-50% on a dried basis, ensuring consistent functionality and safety.
Absorption and Metabolism
E462 functions as a stabilizer and thickener; detailed absorption data is limited.
Like other cellulose derivatives, E462 does not accumulate in the body and is generally considered safe because it functions locally in food systems rather than being systemically absorbed.
Potential Side Effects
At normal food use levels, no adverse effects are documented.
E462 is generally well-tolerated. At very high quantities far exceeding normal food consumption, theoretical mild gastrointestinal effects might occur, similar to consuming excessive dietary fiber. Allergic reactions are extremely rare.
Comparison with Other Cellulose Additives
E462 is one of nine cellulose additives with different properties:
– E460: Microcrystalline cellulose (recently linked to CVD in observational study)
– E461: Methyl cellulose
– E462: Ethyl cellulose (this product—water-insoluble) ←
– E463: Hydroxypropyl cellulose (water-soluble)
– E464: Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (water-soluble)
– E465: Ethyl methyl cellulose (water-soluble)
– E466: Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (water-soluble, restricted for infants)
– E468: Cross-linked sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
– E469: Enzymatically hydrolysed carboxymethyl cellulose
E462 is unique among these in being water-insoluble—a key property for its specialized applications.
Regulatory Approval Across Regions
E462 approval is nearly universal:
– United States (FDA): GRAS—Generally Recognized As Safe (approved 2013)
– European Union (EFSA): Approved food additive, Quantum Satis use
– International (JECFA): FAO/WHO approved with ADI “not specified”
This universal approval reflects confidence in its safety across different regulatory systems.
Feed Additive Status
E462 is approved as a feed additive for all animal species.
It can be used without minimum or maximum content requirements, further demonstrating regulatory confidence in its safety.
The Bottom Line
E462 (ethyl cellulose) is a plant-based thickener, stabilizer, and film former used in dietary supplements, sauces, salad dressings, and processed foods.
Regulatory authorities worldwide classify it as safe, with the FDA rating it GRAS and the EFSA confirming “no safety concern at reported uses and use levels.”
The EFSA’s 2017-2018 re-evaluation found no numerical ADI is needed—indicating exceptional safety.
At normal food use levels, actual exposure is far below any threshold for concern.
E462’s distinctive water-insoluble property makes it particularly valuable for creating protective coatings and moisture barriers—functions that water-soluble celluloses cannot fulfill as effectively.
E462 has decades of safe use in medications, providing real-world evidence of safety in human consumption.
E462 is entirely plant-based and suitable for vegan, vegetarian, gluten-free, and kosher diets.
Most people consuming dietary supplements or processed foods consume E462 regularly without documented health concerns.
As always, food labels must declare E462 when used, enabling informed consumer choice.