What is E579?
Complete guide to understanding E579 (Ferrous Gluconate) — an iron nutrient fortification additive used for black olives and iron supplementation, currently undergoing EFSA re-evaluation
The Quick Answer
E579 (Ferrous Gluconate) is an iron nutrient additive used to darken black olives and fortify foods with iron — approved by FDA, EFSA, and JECFA, currently undergoing EFSA re-evaluation as part of comprehensive gluconic acid assessment program.
What makes E579 fundamentally different from all previous additives: E579 is the first additive in this research collection that is a NUTRIENT fortification agent, not a functional additive (anti-caking, coloring, etc.). Iron is essential to human nutrition; ferrous gluconate is a bioavailable form of iron used both in pharmaceutical supplements for anemia treatment AND in food additive form for olive processing and food fortification. This distinction is critical: while E551-E561 are additives that serve processing functions, E579 is a nutrient that also serves a processing function. E579 bridges the gap between pharmaceutical iron supplements and food additives. Most importantly, EFSA is currently re-evaluating E579 as part of a comprehensive assessment of gluconic acid-based additives (E574-E579), with scientific submissions due in March 2024, meaning E579’s status may be updated or changed based on new evidence.
E579 is unique: a nutrient fortification additive currently undergoing EFSA re-evaluation.
📌 Quick Facts
- Chemical Name: Ferrous Gluconate; Iron(II) Gluconate; Iron(II) di-D-gluconate dihydrate
- Type: Nutrient fortification additive; iron supplement; food additive
- Chemical formula: C₁₂H₂₂FeO₁₄- 2H₂O; Molecular weight: 482
- Appearance: Yellow-gray or light green fine powder or granules
- Primary functions: Black olive darkening; iron fortification; anemia treatment
- EU Status: Approved; currently undergoing EFSA re-evaluation (E574-E579 program)
- FDA Status: Approved for food use; GRAS for iron fortification
- JECFA Status: Approved; PMTDI 0.8 mg/kg body weight (iron)
- Re-evaluation Timeline: EFSA call for data deadline March 31, 2024
- Approved uses: Canned/bottled fruit and vegetables; olives (max 150 mg/l or kg)
What Exactly Is E579?
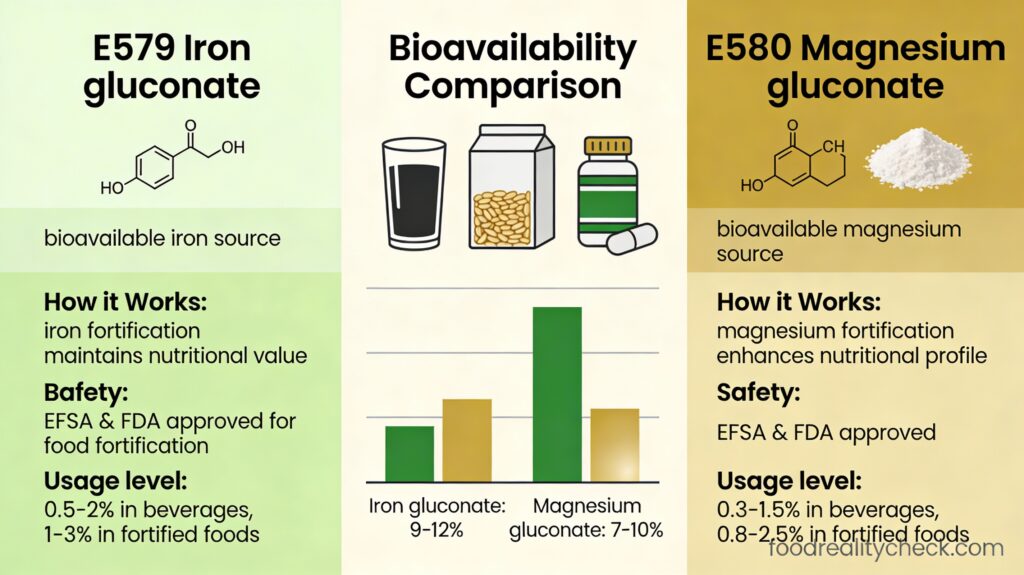
E579 is ferrous gluconate, an iron salt of gluconic acid used as a nutrient fortification additive for black olives and iron supplementation.
Chemical composition: Iron(II) salt of gluconic acid (C₁₂H₂₂FeO₁₄- 2H₂O)
Appearance: Yellow-gray or light green fine powder; insoluble in ethanol, soluble in water
Physical properties:
– Molecular weight: 482
– Specific optical rotation: +6.7° at 25°C
– Forms supersaturated aqueous solutions (stable temporarily)
– Poorly water-soluble but bioavailable when ingested
– Contains iron in +2 (ferrous) oxidation state
Key properties (functional):
– Highly bioavailable iron source (superior to some iron salts)
– Darkens olives through oxidation (distinctive black color)
– Provides iron nutrient for supplementation
– Effective for treating iron-deficiency anemia
– FDA-approved and pharmacopeial standard (USP, EP, BP)
Uses of E579: Nutrient Plus Processing Function
E579 serves both nutritional and functional purposes in food.
| Use Type | Application | Function | Safety Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black olive darkening | Canned/bottled olives (EU approved use) | Oxidizes olives to black color | APPROVED (max 150 mg/l) |
| Iron fortification | Breads, cereals, beverages, supplements | Adds bioavailable iron nutrient | APPROVED (variable limits) |
| Medical/pharmaceutical | Iron supplement tablets, syrups, capsules | Treats iron-deficiency anemia | FDA/pharma approved |
| Color retention | Preserved vegetables | Maintains color in processed vegetables | APPROVED (food additive) |
Primary EU-approved use: Black olives (canned or bottled) processed by oxidation; maximum 150 mg/l or mg/kg
Secondary approved uses: Iron fortification in various food categories with specific maximum levels
EFSA Re-evaluation: Currently Under Assessment
Most important current development: E579 is being re-evaluated as part of comprehensive gluconic acid additive program.
Official EFSA action: Call for data on re-evaluation of gluconic acid (E 574) and related food additives (E575-E579)
Timeline:
– Registration deadline for interested parties: September 15, 2023
– Submission deadline for scientific data: March 31, 2024
– EFSA assessment phase: Following submission deadline
– Status update: Pending completion of assessment
Why re-evaluation? Under EU Regulation 257/2010, all food additives permitted before January 20, 2009 must be re-evaluated by EFSA for safety. E579 was authorized before this date, triggering mandatory re-evaluation.
Assessment scope: Gluconic acid group (E574-E579) re-evaluated together, including:
– E574: Gluconic acid
– E575: Glucono delta-lactone
– E576: Sodium gluconate
– E577: Potassium gluconate
– E578: Calcium gluconate
– E579: Ferrous gluconate (iron nutrient)
Safety Assessment and Tolerances
E579 safety has been established with specific tolerable intake limits for iron.
Regulatory approvals:
– FDA: Approved for food use; GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe)
– EFSA: Approved; currently undergoing re-evaluation
– JECFA: Approved; established Tolerable Intake (see below)
– Australia/New Zealand: Approved (code 579)
– Pharmacopoeias: USP, EP, BP standards for pharmaceutical use
Iron Tolerable Intake (JECFA, 1987):
– PMTDI (Provisional Maximum Tolerable Daily Intake): 0.8 mg/kg body weight
– Basis: Provisional status reflects element approach rather than compound-specific
– Application: Applies to all iron-containing additives and supplements
Toxicity considerations: Iron toxicity recognized only with overdose — important distinction from chronic hazards of other additives
Overdose symptoms (Wikipedia reference): Iron toxicity in children occurs at 10-20 mg/kg elemental iron; serious toxicity at >60 mg/kg. However, normal food use and supplementation are far below these levels.
The Bottom Line
E579 is an iron nutrient fortification additive approved for black olive darkening and iron supplementation — currently undergoing EFSA re-evaluation with assessment ongoing.
Key facts about E579:
– Nutrient function: Provides bioavailable iron essential to human health
– Processing function: Darkens black olives through oxidation
– Medical use: Treats iron-deficiency anemia (pharmaceutical-grade)
– Regulatory approval: FDA approved; EFSA approved (re-evaluation ongoing)
– Safety established: JECFA tolerable intake 0.8 mg/kg body weight for iron
– Current status: Under re-evaluation; assessment pending completion
– Approved uses: Black olives (150 mg/l max); various fortified foods
– Bioavailability: Superior iron absorption compared to some iron sources