What is E580?
Complete guide to understanding E580 (Magnesium Gluconate) — a magnesium nutrient fortification additive with superior bioavailability, currently undergoing EFSA re-evaluation
The Quick Answer
E580 (Magnesium Gluconate) is a magnesium nutrient fortification additive with superior bioavailability — approved by FDA, EFSA, and JECFA, currently undergoing EFSA re-evaluation as part of gluconic acid additive group assessment.
What makes E580 particularly valuable: Unlike most food additives that serve processing functions without nutritional benefit, E580 is a NUTRIENT — it provides magnesium, an essential mineral for human health (involved in nerve signaling, muscle function, bone health, energy metabolism). E580 is specifically noted in scientific literature as having the HIGHEST bioavailability of any magnesium salt, making it superior to magnesium sulfate, oxide, chloride, and other forms. This nutritional advantage is significant: people with magnesium deficiency (common with diuretic use, certain intestinal diseases, poor diet, alcoholism) can absorb E580 magnesium more effectively than other supplemental forms. E580 is currently undergoing the same EFSA re-evaluation program as E579 (iron gluconate), with assessment ongoing following the March 31, 2024 data submission deadline.
E580 is unique: a magnesium nutrient with superior bioavailability, currently undergoing EFSA re-evaluation.
📌 Quick Facts
- Chemical Name: Magnesium Gluconate; Magnesium salt of gluconic acid
- Type: Nutrient fortification additive; magnesium supplement; firming agent
- Chemical formula: Mg(C₆H₁₁O₇)₂; Molecular weight: 450
- Appearance: White to off-white powder or fine granules; soluble in water
- Primary property: HIGHEST oral bioavailability of all magnesium salts
- EU Status: Approved; currently undergoing EFSA re-evaluation (E574-E579 program)
- FDA Status: Approved for food use; GRAS for magnesium fortification
- JECFA Status: Approved; Group ADI (not specified) for gluconic acid salts
- Re-evaluation Status: Part of E574-E579 gluconic acid assessment; ongoing
- Medical use: Treats hypomagnesemia (low blood magnesium); prevents deficiency
What Exactly Is E580?
E580 is magnesium gluconate, a magnesium salt of gluconic acid used as a nutrient fortification additive with superior absorption properties.
Chemical composition: Magnesium salt of D-gluconic acid; Mg(C₆H₁₁O₇)₂
Appearance: White to off-white fine powder or granules; hygroscopic (absorbs moisture)
Physical properties:
– Molecular weight: 450
– Highly soluble in water
– Hygroscopic nature (requires moisture protection)
– LogP: -3.175 (hydrophilic)
– Magnesium content: approximately 5.3%
Key functional properties:
– HIGHEST bioavailability of magnesium salts (superior absorption)
– Causes minimal gastrointestinal side effects (less diarrhea than other Mg forms)
– Effective for treating magnesium deficiency (hypomagnesemia)
– Firming agent in foods (maintains texture in processed foods)
– Essential nutrient delivery (magnesium for nerve, muscle, bone health)
– Pharmaceutical-grade quality (USP, BP standards)
Medical and Nutritional Uses of E580
E580 serves both medical and nutritional functions in treating magnesium deficiency.
Medical uses (pharmaceutical):
– Treatment of hypomagnesemia (low blood magnesium)
– Prevention of magnesium deficiency in at-risk populations
– Management of magnesium depletion from diuretics
– Treatment of magnesium deficiency from gastrointestinal disorders
– Cardiac arrhythmia treatment (in combination with potassium gluconate)
– Prevention of pregnancy-induced hypertension
– Reduction of premature uterine contractions
Food fortification uses:
– Mineral fortification in various food categories (regulatory approval)
– Firming agent in canned/bottled fruits and vegetables
– Dairy product fortification (milk, yogurt, cheese enrichment)
– Beverage fortification with bioavailable magnesium
– Nut product fortification (supplemental magnesium)
Why magnesium matters:
Magnesium is essential for: nerve function, muscle contraction, bone health, energy metabolism, protein synthesis, cardiovascular function. Magnesium deficiency is common, caused by diuretics, gastrointestinal disorders, poor diet, alcoholism, or certain medical conditions.
EFSA Re-evaluation Status: Part of Gluconic Acid Group Assessment
E580 is undergoing the same re-evaluation program as E579 (ferrous gluconate) — comprehensive assessment of gluconic acid additives.
Re-evaluation program details:
– Scope: E574-E579 gluconic acid additives assessed as a group
– Timeline: EFSA call for scientific data; submission deadline March 31, 2024
– Status: Assessment in progress following data submission
– Additives included: E574 (gluconic acid), E575 (glucono delta-lactone), E576 (sodium gluconate), E577 (potassium gluconate), E578 (calcium gluconate), E579 (ferrous gluconate), E580 (magnesium gluconate)
Why re-evaluation? Under EU Regulation 257/2010, all food additives authorized before January 20, 2009 must be re-evaluated using current scientific standards. E580 was authorized before this date, triggering mandatory re-evaluation with other gluconic acid salts.
What may change: Safety assessment could be updated, modified use conditions established, or approval maintained based on current evidence and new submissions.
Safety Assessment and Regulatory Status
E580 safety has been established with regulatory approvals from major food safety authorities.
Regulatory approvals:
– FDA: Approved for food use; GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe)
– EFSA: Approved; undergoing re-evaluation (ongoing)
– JECFA: Approved; Group ADI for gluconic acid additives (not specified individually)
– Australia/New Zealand: Approved as food additive
– Pharmacopoeias: USP (United States Pharmacopoeia), BP (British Pharmacopoeia) standards
JECFA Assessment (1998):
– Evaluation: Group ADI for glucono delta-lactone, calcium gluconate, magnesium gluconate, potassium gluconate, and sodium gluconate
– ADI Status: NOT SPECIFIED (group evaluation; element-based approach)
– Basis: JECFA 51/46 (Report TRS 891)
Safety considerations:
– Magnesium toxicity occurs only with excessive intake (>5 g/day) and kidney dysfunction
– Normal kidney function allows effective magnesium excretion
– Food fortification levels far below toxicity thresholds
– Gastrointestinal side effects (diarrhea) more likely than systemic toxicity
– Therapeutic window very wide (unlike many pharmaceutical substances)
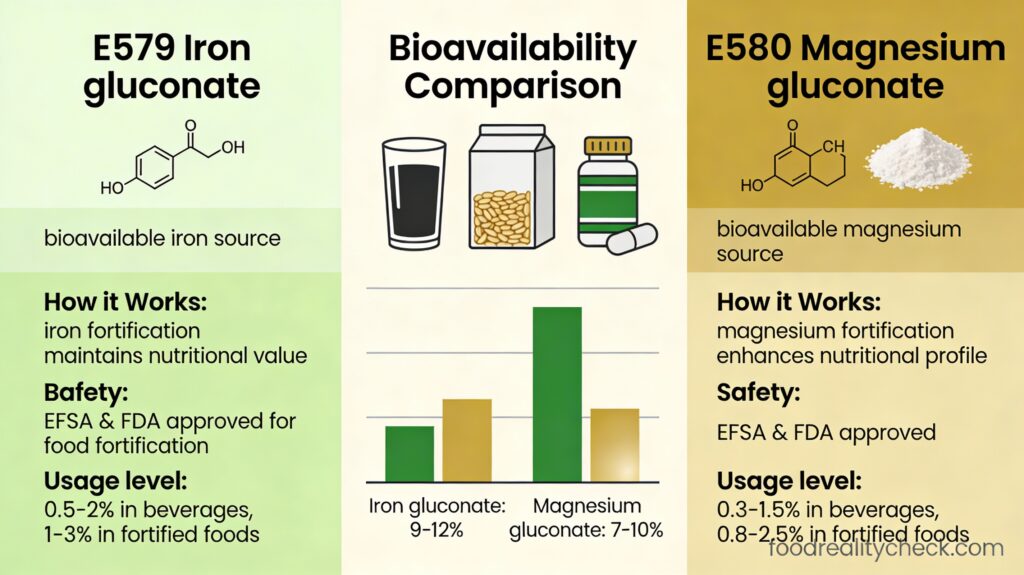
Comparison: E580 vs E579 (Gluconic Acid Group)
E580 and E579 are both nutrient fortification additives undergoing the same EFSA re-evaluation.
| Characteristic | E579 (Ferrous Gluconate/Iron) | E580 (Magnesium Gluconate) |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient type | Iron (trace element) | Magnesium (essential mineral) |
| Primary nutrient role | Oxygen transport; hemoglobin formation | Nerve/muscle function; bone health; energy |
| Bioavailability advantage | Good absorption; forms complex with proteins | HIGHEST of all magnesium salts (superior) |
| Processing function | Black olive darkening | Firming agent in fruits/vegetables |
| Side effect profile | Gastrointestinal (dark stools, constipation) | Gastrointestinal (diarrhea less likely than other Mg) |
| Re-evaluation status | Part of E574-E579 group assessment | Part of E574-E579 group assessment |
| Data deadline (passed) | March 31, 2024 | March 31, 2024 |
| Current status | Assessment ongoing | Assessment ongoing |
The Bottom Line
E580 is a magnesium nutrient fortification additive with superior bioavailability — approved globally, currently undergoing EFSA re-evaluation as part of gluconic acid group assessment.
Key facts about E580:
– Nutrient function: Provides bioavailable magnesium essential for health
– Superior bioavailability: Highest magnesium absorption of all magnesium salts
– Processing function: Firming agent in preserved foods
– Medical use: Treats hypomagnesemia and prevents magnesium deficiency
– Regulatory approval: FDA, EFSA, JECFA, Australia/New Zealand approved
– Safety established: JECFA group ADI; no acute toxicity concerns at food levels
– Re-evaluation status: Under assessment with E574-E579 gluconic acid group; ongoing
– Approval may change: Based on new evidence emerging during 2024 re-evaluation